
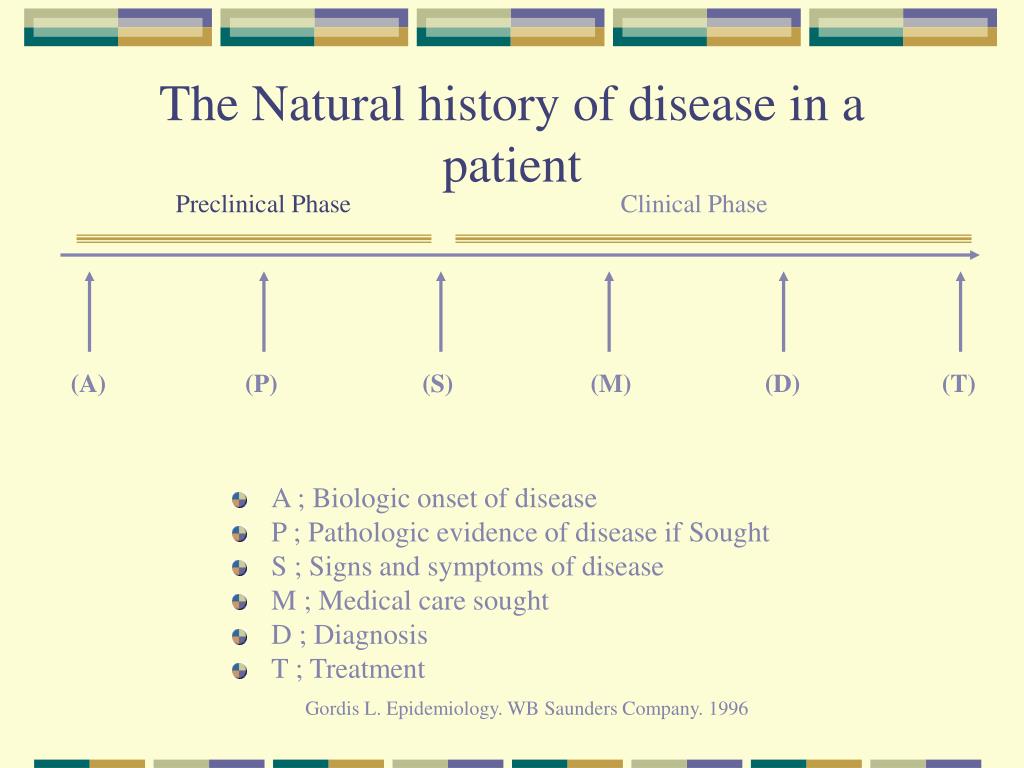
There are two complementary perspectives for characterizing the natural history of disease. In regards to the natural history of disease, the goal of the medical field is to discover all of the different phases and components of each pathological process in order to intervene as early as possible and change the course of the disease before it leads to the deterioration of a patient's health. It constitutes the course of biological events that occurs during the development of a disease from its root causes ( etiology) to its outcome, whether that be recovery, chronicity, or death. The subclinical (pre-symptomatic) and clinical (symptomatic) evolution of disease is the natural progression of a disease without any medical intervention. Because these medications can alter the natural history of disease, they are referred to as disease-modifying antirheumatic drug. There are no treatments that can modify that auto-immune inflammatory process (immune modulating drugs) that can slow the progression of the disease. In contrast, consider rheumatoid arthritis, a systemic inflammatory disease that damages articular cartilage throughout the body. There are only palliative/symptomatic treatments such as analgesics and exercises. There are no disease-modifying treatments for osteoarthritis-no way to slow, arrest, or reverse this pathophysiological process. Īs an example, the cartilage of the knee, trapeziometacarpal and other joints deteriorates with age in most humans (osteoarthritis). Natural history of disease is one of the major elements of descriptive epidemiology. Knowledge of the natural history of disease ranks alongside causal understanding in importance for disease prevention and control. The natural history of a disease is sometimes said to start at the moment of exposure to causal agents. The inception of a disease is not a firmly defined concept.

The natural history of disease is the course a disease takes in individual people from its pathological onset ("inception") until its resolution (either through complete recovery or eventual death).

You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation.If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article. Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality.
Consider adding a topic to this template: there are already 5,106 articles in the main category, and specifying |topic= will aid in categorization.Machine translation like DeepL or Google Translate is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
